In reflection of the Australia's grievous history with its Indigenous people, Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced the country's national anthem would be altered from January 1.
Australia will no longer be referred to as “young and free” in the anthem. Instead, people will sing “one and free,” in hopes it will create a “spirit of unity” among its inhabitants and acknowledge people who have lived in Australia tens of thousands of years before colonists.
Prime Minister Morrison claimed, “it recognizes the distance we have travelled as a nation. It recognizes that our national story is drawn from more than 300 national ancestries and language groups and we are the most successful multicultural nation on earth.”
While the gesture has been recognised as an important step, the Indigenous peoples of Australia continue to face structural racism and discrimination in criminal justice, education and health.
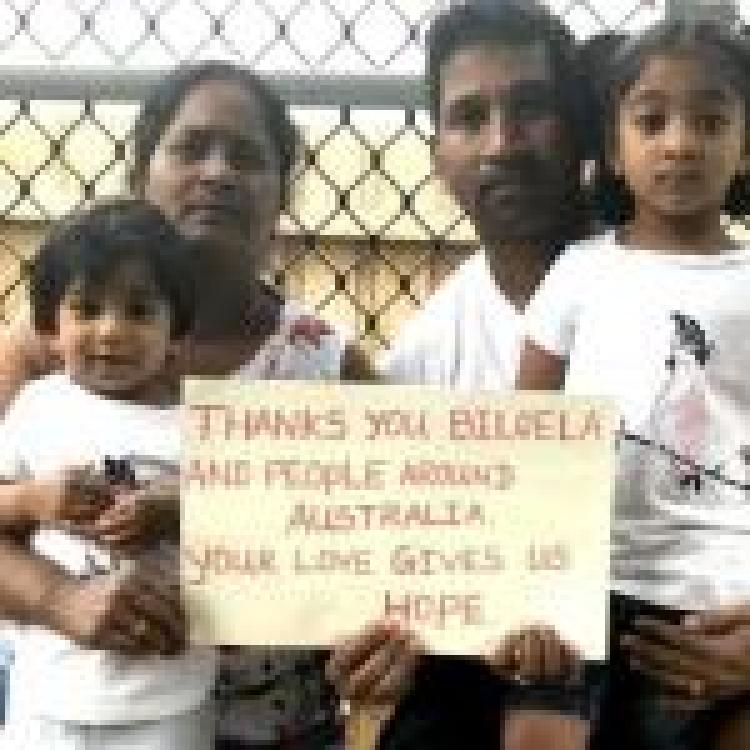
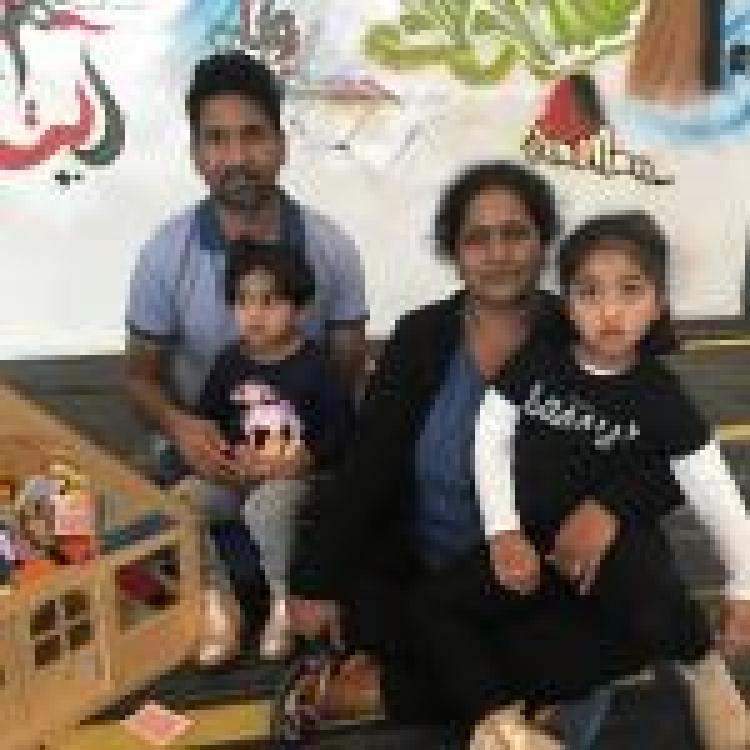
Australia's draconian immigration and asylum policies also belie Morrison's claim to successful multiculturalism. A Tamil family has been detained on Christmas Island for 1000 days in a one-bedroom cabin and continues to face deportation to Sri Lanka despite valid concerns over torture and extra-judicial killings in Sri Lanka. Australia’s Department of Home Affairs has repeatedly maintained the family does not meet the criteria for protected status.
Morrison also added that the change to the anthem celebrated the unity Australia saw during the coronavirus pandemic.
Australia has been more conscientious of managing disproportionate effects of coronavirus on Indigenous Australians in comparison with the U.S. after Indigenous Australians were devastated by the H1N1 influenza epidemic in 2009. However, these recommendations for immediate action in Indigenous-populated areas were taken because of greater risk factors. Many Indigenous people live in remote areas and suffer from higher chronic disease rates because of marginalization from health services, food insecurity, and inadequate access to water, sanitation, and housing making social distancing and self-isolation practices more unrealistic.
Extraordinary efforts taken by First Nations health leaders of Aboriginal Community Controlled Health Services (ACCHOs) have contributed to considerable underrepresentation of Indigenous cases, representing only 0.7% of all cases according to a study published by The Lancet.