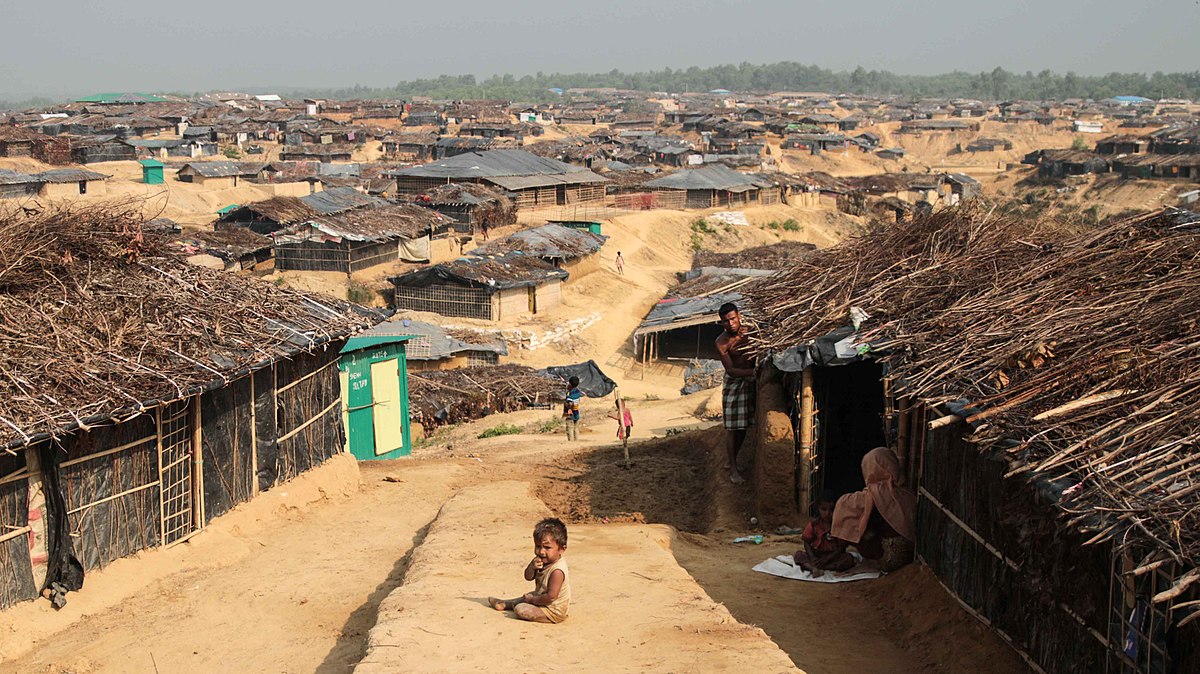
File photograph: Rohingya refugees at a camp in Bangladesh (VOA/John Owens)
India has engaged in an increased crackdown on border crossings from Bangladesh leading to the arrest and deportation of dozens of Rohingya Muslims this year.
An estimated 40,000 Rohingya Muslims have sought shelter in India from the on-going violence they face in Myanmar. Of the approximate 40,000, the UNHRC estimates 18,000 have registered as refugees.
Al Jazeera notes that since the beginning of this year “at least 1,300 Rohingya […] have crossed into Bangladesh from India” in 2019 alone.
India though, has responded with an increased focus on detaining those crossing the border and deporting them back to Myanmar. On October 4th 2018 India deported seven Rohingya, who were jailed for ‘illegally crossing’ in Assam State in 2012. Last week an approximate 61 Rohingya were arrested and on Tuesday another 31 were arrested in the land dividing India and Bangladesh.
This response has evoked international outcry from organisations such as Human Rights Watch and the Zakat Foundation, accusing the government of breaking with the internationally recognised principle of non-refoulement, which stipulates a responsibility to protect refugees and not to deport those who may face persecution in their home country. Zakat has gone further as to accuse the ruling Hindu nationalist BJP government decision to deport Rohingya, of being driven by anti-Muslim politics.
Speaking on this issue Nalin Kohli, a spokesperson for the Bharatiya Janata Party, refused to grant refugee status to the Rohingya stating that New Delhi was not a signatory to international protocols.
Kohli further stated, "We do not want to opine on whether Myanmar is safe for Rohingya or not… Myanmar government has said they are willing to take them back”.
Adding to his remarks he claimed that the current Rohingya populous posed a "big security threat".
The crackdown comes as AK Abdul Momen, Bangladesh's newly appointed foreign minister, will be visiting India soon to discuss the refugee crisis further.
See more from Al Jazeera here.