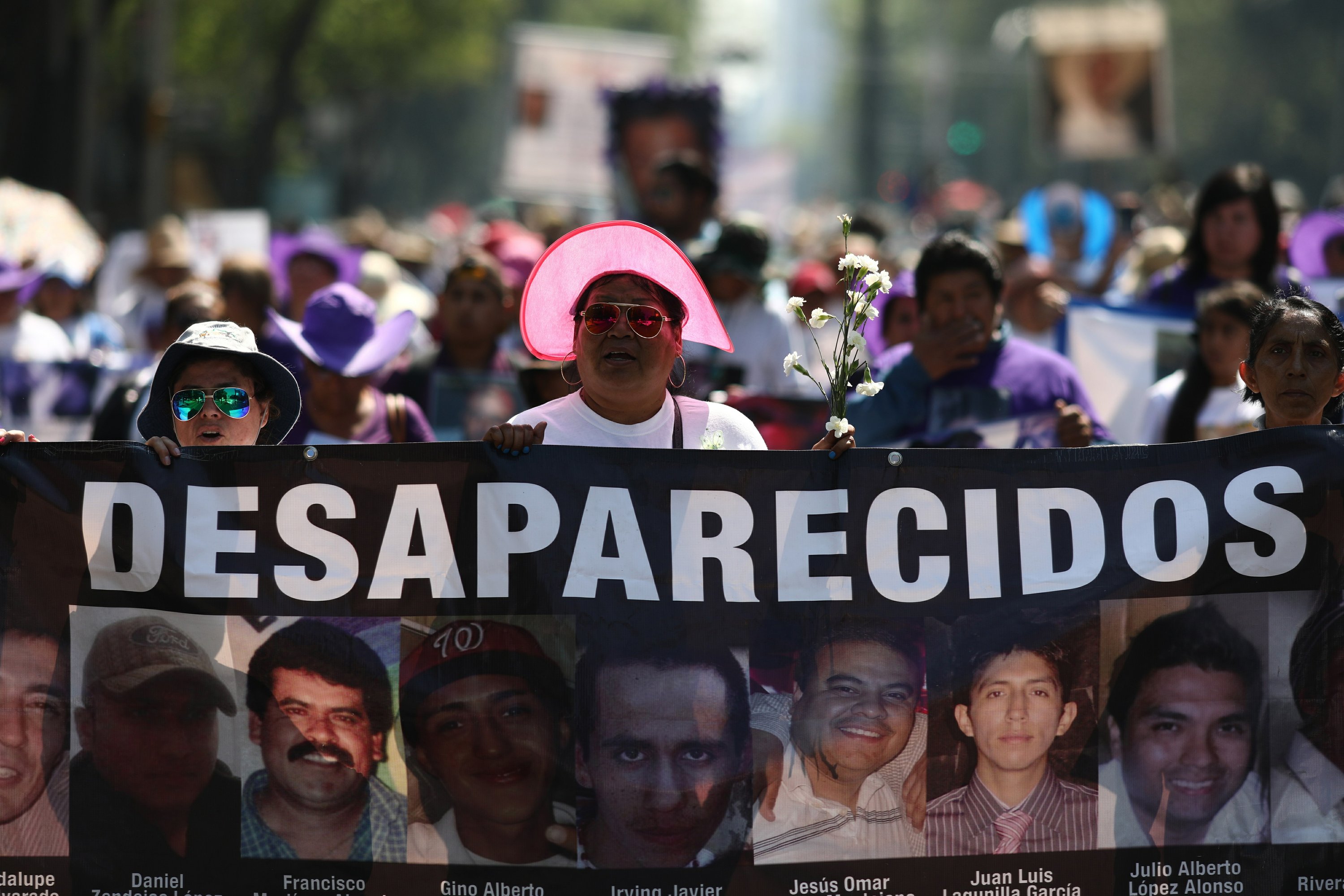
Activists say the review of 113,000 missing people in Mexico is a ploy to reduce the number ahead of the presidential election
The government has now announced it was able to confirm just 12,377 of the more than 113,000 cases of disappeared people.
The registry had become intensely politicised, with the rising number of disappeared a symbol of the continuing insecurity across the country, while the Mexican president, Andrés Manuel López Obrador, said that it was being inflated to attack the government.
Violence in Mexico soared with the launch of the militarised “war on drugs” in 2006, and it has remained stubbornly high throughout the term of López Obrador, popularly known as Amlo, which began in 2018.
That same year, the National Search Commission was established to look for disappeared people, working with local commissions and prosecutor’s offices in each state, and regularly publishing the accumulating number of cases in its registry.
Amlo promised a change in security strategy, but has failed to deliver improvements, and the ever-climbing number of disappeared – along with the number of homicides, which in 2022 topped 30,000 for the fifth year in a row – have been a frequent line of attack on his government.
In June, Amlo announced a “census” to review the official total of disappearances, case by case.
Karla Quintana, who had led the National Search Commission since 2019, resigned shortly after that announcement. “Their intention is very clear and it is regrettable: it is to reduce the number of disappeared people, mainly during this government,” said Quintana soon afterwards.
Quintana was replaced by Teresa Guadalupe Reyes Sahagún, who before that had been the general director of the National Institute for Adult Education.
The UN’s human rights office in Mexico criticised the process by which Reyes was appointed, citing a lack of consultation, transparency and scrutiny.
“I think the National Search Commission had important support from the government in the first few years,” said Pérez Ricart. “And now the impression is that the commission is at the service of the president.”
Little information was made public about the methodology with which the commission was updating the registry.
In a statement this week, some collectives of family members of missing people rejected the update, “because without transparency they are disappearing the disappeared”.
“The data is a mess. That’s the reality,” said Pérez Ricart. “[The registry] was an important effort, and I think Karla Quintana was a great civil servant, who did everything she could. But we are talking about a project that regrettably failed, and one that now has very little legitimacy.”
Meanwhile, the underlying phenomenon of disappearances remains poorly understood.
“Various important [questions] remain in the air,” wrote Jacobo Dayán, an investigator and columnist. “Who are these people? Where are they? Who is responsible for their disappearance? Why did they disappear? Why is it not being investigated?”
And the violence and insecurity in Mexico continue unabated.
“Instead of trying to score political points by disputing the number of disappeared, the president should listen to the thousands of families clamouring for justice and take steps to address the systemic causes of this ongoing catastrophe,” said Tyler Mattiace, a Mexico researcher at Human Rights Watch.
Read more at Guardian
 The UK government is facing accusations of hypocrisy for not supporting South Africa's case accusing Israel of committing genocide against Palestinians in Gaza.
The UK government is facing accusations of hypocrisy for not supporting South Africa's case accusing Israel of committing genocide against Palestinians in Gaza.