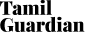Tamil Brahmi inscription found in Tissamaharama
An early historic inscription in Tamil language and in Tamil Brahmi script, dateable to c.200 BCE, has been found in the archaeological excavations by a German team at Tissamaharama in the south of the
The inscription deciphered by I. Mahadevan as ‘Thira’li Mu’ri,’ which means ‘written agreement of the assembly,’ was incised on an early historic Black and Red Ware pottery.
The last letter of the inscription, which is retroflex Tamil ‘Ri’, is very clearly a Tamil phoneme in Tamil Brahmi script, academics commented. The Tamil Brahmi inscription is also found mixed with megalithic or early historic graffiti marks, which were probably the symbols of the guild, they further said.
Tissamaharama or ancient Mahaagama is located close to Kathirkaamam (Kataragama), a famous pilgrim centre for Tamils as well as Sinhalese.
Prakrit and Tamil were the earliest written languages of
Sinhala as an identifiable language appears in inscriptions from c. 8– 9th century CE onwards.
The following is what Iravatham Mahadevan, doyen of the study of Tamil Brahmi, wrote on Tissamaharama potsherd inscription in The Hindu, Thursday:
“Tamils have been living in the northern and eastern parts of the island from time immemorial. Several small fragments of pottery with a few Tamil‐Brahmi letters scratched on them have been found from the
Writing on “An Epigraphic perspective on the Antiquity of Tamil.” Mahadevan cited the American scholar Thomas Trautmann and said: “The three ‘fundamental discoveries’ in indological studies are the discovery of the Indo-European language family (1786); the discovery of the Dravidian language family (1816), and the discovery of the
Mahadevan continues: “Part of the problem in the delayed recognition accorded to Tamil in Indological studies was the non‐availability of really old literary texts and archaeological evidence for the existence of Tamil civilisation in ancient times. The critical editions of the earliest Tamil literary works of the Sangam Age, especially by U.V. Swaminathaiyar from 1887, have led to a radical reassessment of the antiquity and historicity of Tamil civilisation. What Swaminathiyar did for Tamil literature, K.V. Subrahmanya Aiyer accomplished for Tamil epigraphy. He demonstrated (in 1924) that Tamil (and not Prakrit) was the language of the cave inscriptions of Tamil Nadu..”
Eelam Tamil academics sadly commenting on the repeated assertions of Mahadevan in giving exclusive credit to Swaminathaiyar for the publication of Changkam literature and not giving due credit to the efforts of Eelam Tamils, said scholars from Jaffna did the pioneering work decades before Swaminathaiyar.
The first ever Changkam text that saw the light of print was Thirumurukaattuppadai of Paththuppaaddu (one of The Ten Idylls), which was brought out by Arumuga Navalar of
The first of the Eight Anthologies (Edduththokai) of the Changkam classics that got printed was Kaliththokai (1887). This was brought out by C.W. Thamotharam Pillai of
Swaminathaiyar brought out his first edition of the Changkam classics Paththuppaaddu in 1889.
Earlier to bringing out Kaliththokai, Thamotharam Pillai started publishing post-Changkam classics such as Choo'laama'ni, Tholkaappiyam etc right from 1860's.
The book of V. Kanagasabai Pillai of Trincomalee, The Tamils 1800 Years Ago (1904), was the first major historical and social study on the Changkam Age, based on the classics.
The pioneering work of translating the Changkam classics into English, bringing the text to non-Tamil readers, was also done by Eelam Tamil scholars.
J V Chellaiah of Jaffna College did the entire translation of Paththuppaaddu in 1945. This was decades before A K Ramanujan or Hart translating parts of the Eight Anthologies.
Swami Vipulanandar of Batticaloa who made arrangement for the publication of Chellaiah’s translation painfully notes how the then Madras government or the Annamalai university didn’t give any help to the venture even though they admired the translation, and how he finally brought it out as a publication of the government press of then British Ceylon.